
This feature is not supported by this version of ArubaOS.
Query switch for mac table snmp password#
Snmp-server host ipaddr version password priv-prot DES passwordĮarlier versions of ArubaOS supported SNMP on individual APs. If you are using SNMPv3 to obtain values from the controller, click Add in the SNMPv3 Users section to add a new SNMPv3 user.
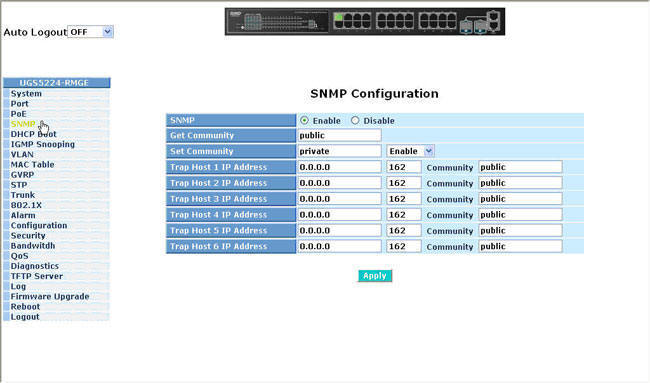
If the controller will be sending SNMP traps, click Add in the Trap Receivers section to add a trap receiver. Navigate to the Configuration > Management > SNMP page. Check Using Command Line (CLI) Check Using Web GUI Step 1: Click Network Administration -> Port Settings -> Address Tables Step 2: Click 'Dynamic Address Table' to check the mac address of all devices connected to this switch. If messages sent on behalf of this user can be encrypted/decrypted with DES, the (private) privacy key for use with the privacy protocol.įollow the steps below to configure a controller’s basic SNMP parameters. We can find the mac address of the devices connected to the switch by using following methods. This takes the value DES (CBC-DES Symmetric Encryption Protocol). This is a string password for MD5 or SHA depending on the choice above.Īn indication of whether messages sent on behalf of this user can be protected from disclosure, and if so, the type of privacy protocol which is used. The physical address (MAC address) for the interface through which the. If messages sent on behalf of this user can be authenticated, the (private) authentication key for use with the authentication protocol. Discovery for SNMP-Enabled Routers, Switches, and Firewalls. SHA: HMAC-SHA-96 Digest Authentication Protocol MD5: HMAC-MD5-96 Digest Authentication Protocol If you are using SNMPv3 to obtain values from the controller, you can configure the following parameters:Ī string representing the name of the user.Īn indication of whether messages sent on behalf of this user can be authenticated, and if so, the type of authentication protocol used. This is optional, and will use the default port number if not modified by the user. UDP port on which the trap receiver is listening for traps. Type: Trap or Inform (SNMP v2c or SNMPv3 only) Configure the following for each host/trap receiver: This host needs to be running a trap receiver to receive and interpret the traps sent by the Aruba controller. Refer to the list of traps in the “SNMP traps” section below for a list of traps that are generated by the controller. NOTE: This is needed only if using SNMP v2c and is not needed if using version 3.Įnables generation of SNMP traps to configured SNMP trap receivers. Querying the Mapping Between MAC Addresses and Interfaces Query existing MAC address entries on the device using dot1dTpFdbAddress. String to describe the location of the controller.Ĭommunity strings used to authenticate requests for SNMP versions before version 3. Name of the person who acts as the System Contact or administrator for the controller. Table 1: SNMP Parameters for the Controller If there is no Cisco MIB to find the total MAC address count then we cant do much either,we rely on SNMP data like every other NMS. You can configure the following SNMP parameters for the controller.
See the ArubaOS MIB Reference Guide for information about the Aruba MIBS and SNMP traps.

MIB Reference Guide for information about the Aruba MIBs and SNMP traps.Īruba-specific management information bases (MIBs) describe the objects that can be managed using SNMP. In other words, SNMP cannot be used for setting values in a n Aruba system in the current ArubaOS version. This is done before scanning the network, so at the time of scanning the application already knows which IP address corresponds to which MAC address and can display them.Aruba controllers support versions 1, 2c, and 3 of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) for reporting purposes only. Your router needs to support at least one of these, have SNMP enabled and a community string set.Īfter enabling the Router SNMP MIB query option, double-click the option and specify a read community string (similar to a password) and the router's IP address, as shown below.Īfter that, the Network Scanner will attempt to make an SNMP connection to the specified IP address(es) using the community string as a password and, if successful, enumerate the above tables that contain IP-to-MAC-address mappings. There are three common OIDs (Object Identifiers) where SNMP-capable routers keep IP-to-MAC-address mapping tables: The router may need to be specially configured to provide this information via SNMP. Since a router sits between subnets and knows clients MAC addresses on each side, this method works for both local and non-local subnets. In this case the Network Scanner can pull the router's ARP tables and match IP addresses to MAC addresses. It is possible to resolve MAC addresses in a different subnet if the router between the subnets exposes its ARP cache via SNMP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
